Back pain (acute motor loss)
Definition/Description
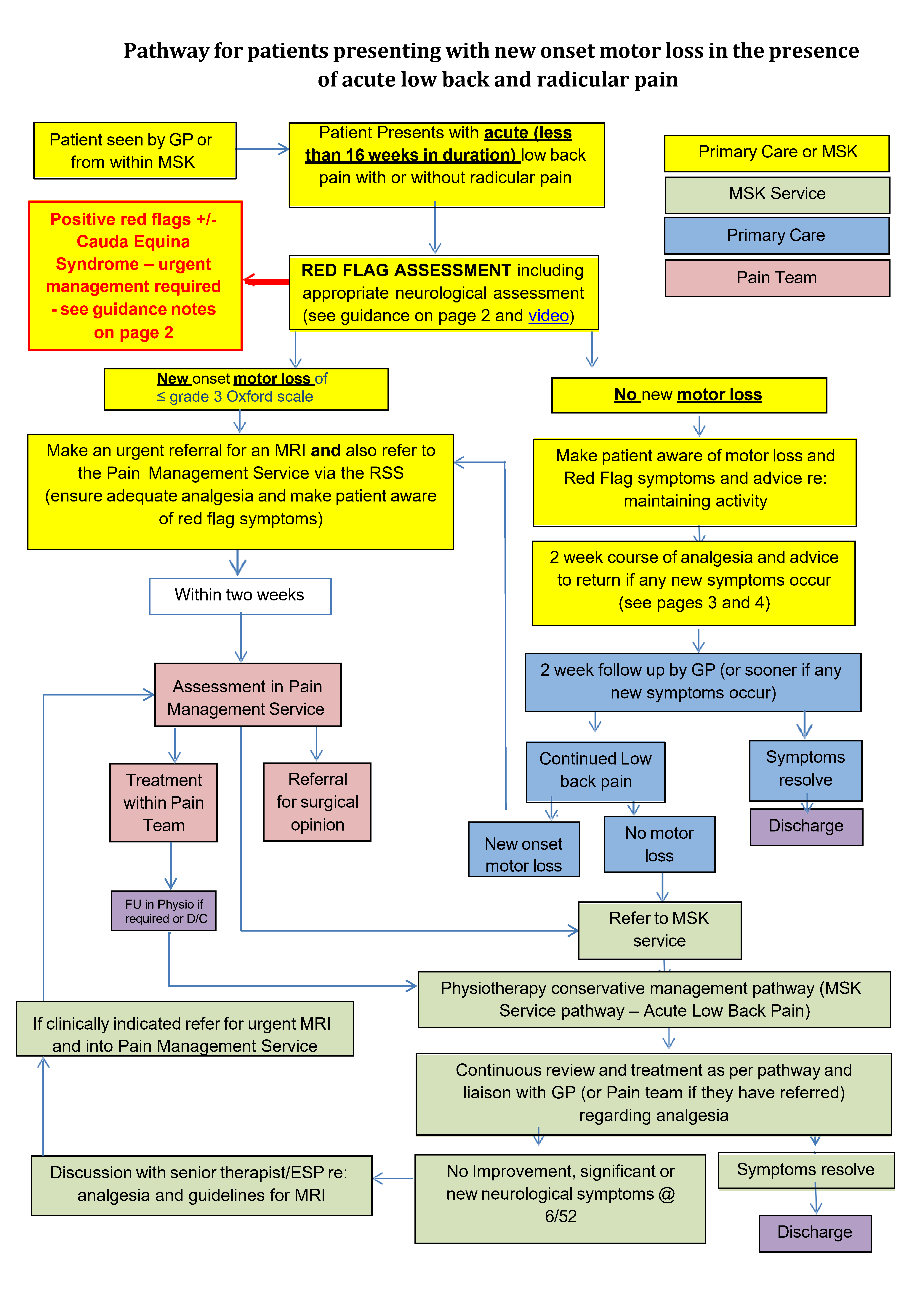
Patient who presents with acute (less than 16 weeks in duration) low back pain with or without radicular pain
Red Flag Symptoms
Red flags where further investigation in primary or secondary care should be considered before referral to MSK:
- Significant motor weakness e.g. Isolated foot drop
- Progressive neurological deficit in lower extremities
- Saddle area numbness, urinary incontinence/retention or faecal incontinence that is not present on day of attendance or are greater than 3 months in duration
- Bilateral true sciatica
- Sexual dysfunction
- Paresis (gait disturbance)
- Thoracic pain
- Weight loss care
- Fever
- Previous malignancy
- Age < 20 or >55
- Systemic illness pain
- HIV
- IV drug user
- Frequent or long term steroid use
- Structural deformity
Cauda Equina syndrome (see pathway guidance)
Symptoms which are present on the day of attendance and are less than 3 months in duration requiring urgent action:
- Altered sensation in the saddle area
- Bladder dysfunction – incontinence or retention
- Faecal incontinence
Guidelines on Management
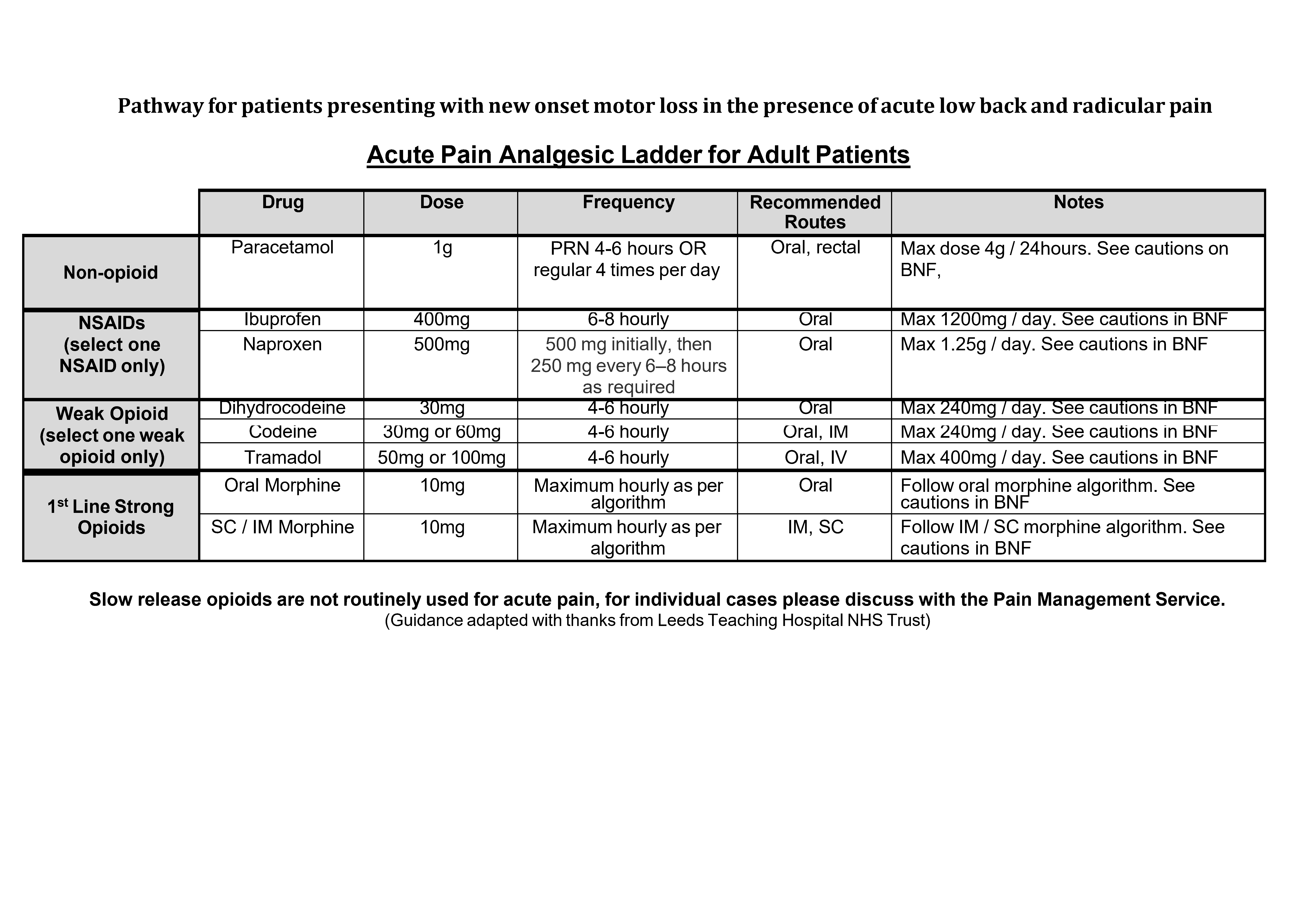
Suggested Acute Pain Analgesic Ladder for Adult Patients
PAIN INTENSITY SCORE 0 No pain |
PAIN INTENSITY SCORE 1 Mild pain |
PAIN INTENSITY SCORE 2 Moderate pain |
PAIN INTENSITY SCORE 3 Severe pain |
|
Regular
PRN
Taper down as symptoms improve |
||||
Regular
PRN |
||||
Regular
PRN |
||||
PRN Paracetamol +/ - ibuprofen |
Cautions: Use the BNF for guidance and cautions.
In addition:
- Be cautious combining weak and strong opiates
- Anti emetics may need to be prescribed with opioids if there are concerns about opioid induced nausea
- Aperients should also be considered with opioids if there are concerns about opioid induced constipation
- Codeine is contraindicated breast feeding mothers
- Check renal function is not impaired when prescribing NSAIDs
- Consider gastric protection when prescribing NSAID’s
(Please also see Image A below)
Referral Criteria/Information
Referral criteria for MRI For MSK physiotherapists:
- Discuss with senior therapist/ESP re: analgesia ladder and patient history (if referring from within MSK)
- The MRI scan will be used to aid decision making for further treatment interventions (either in the Pain team or Orthopaedic surgery)
- Clear neurological deficit (motor loss) in the presence of back pain with radicular symptoms
- It is essential that the MRI request states whether there has been previous back surgery, including the level operated on and when the surgery was. If the patient has had a previous scan of the same area we need to know when and where.
- Check MRI is not contraindicated (no pacemakers, no aneurysm clips, no inner ear implants, no implanted spinal cord stimulators, no metal fragments in the eye).
Additional Resources & Reference
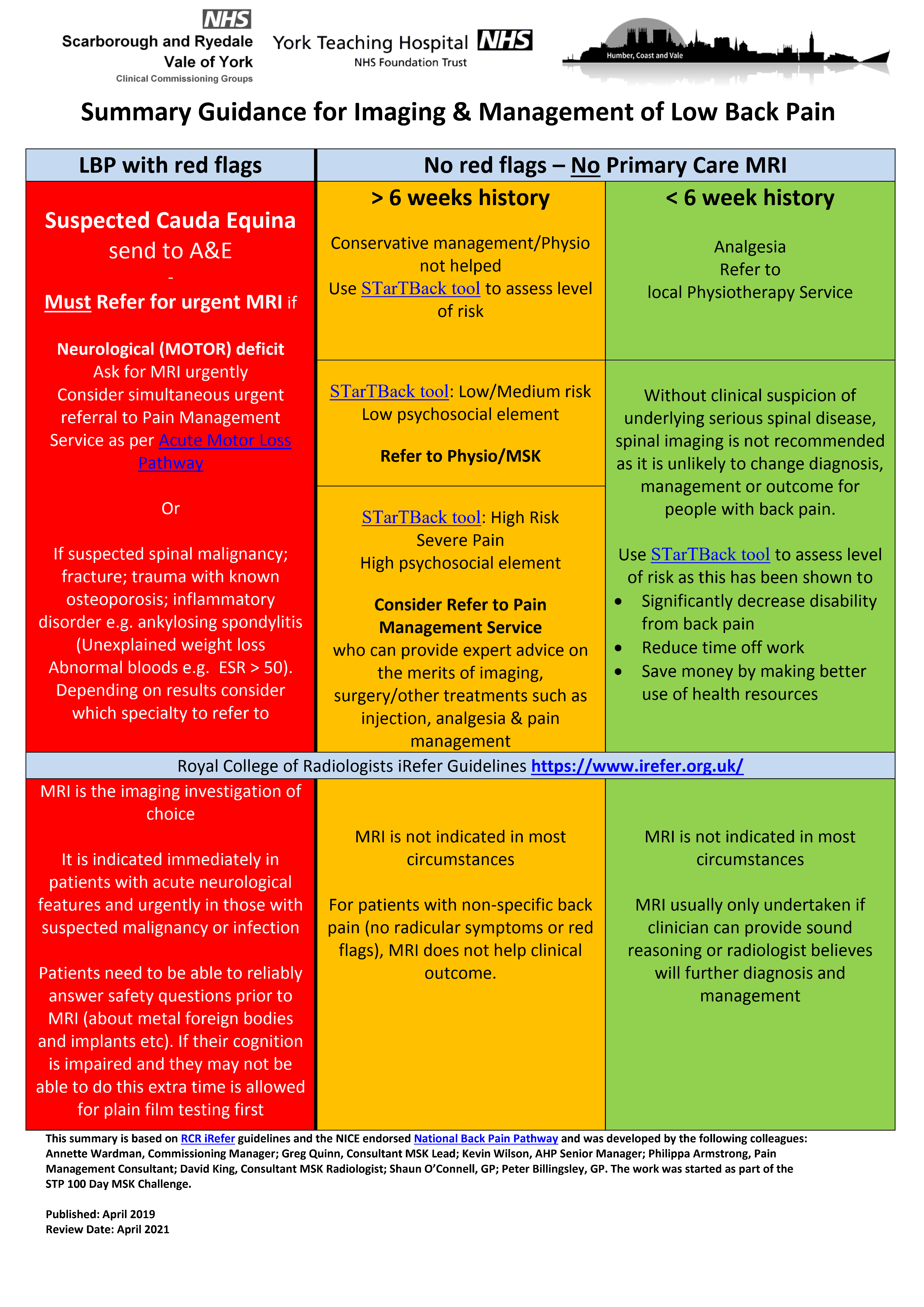
Guidance for back pain pathways:
- Summary guidance for imaging and management of back pain (See also Image C below)
- Cauda equina syndrome
- Lumbar spine
Referral form
Patient information
Any Other Information
Remember…
Referral to hospital for imaging medicalises what is a effectively a normal part of life and ageing
Imaging will be abnormal in the population in proportion to your age Surgery has no role in degenerative back pain
The Cauda Equina Syndrome (CES) UK Charity will provide GPs with credit card size reminders of the symptoms that may be due to developing CES. Safety net with them.
Associated Policies
Specialties
Places covered by
- Vale of York
Hospital Trusts
York and Scarborough Teaching Hospitals