Acute otitis media (AOM)
Definition/Description
Presence of inflammation in the middle ear, associated with an effusion and accompanied by the rapid onset of clinical features of an ear infection
Uncomplicated: mild pain of <4 days and an absence of red or amber features
Complicated: severe pain, bilateral infection, mastoiditis, labyrinthitis, facial nerve palsy
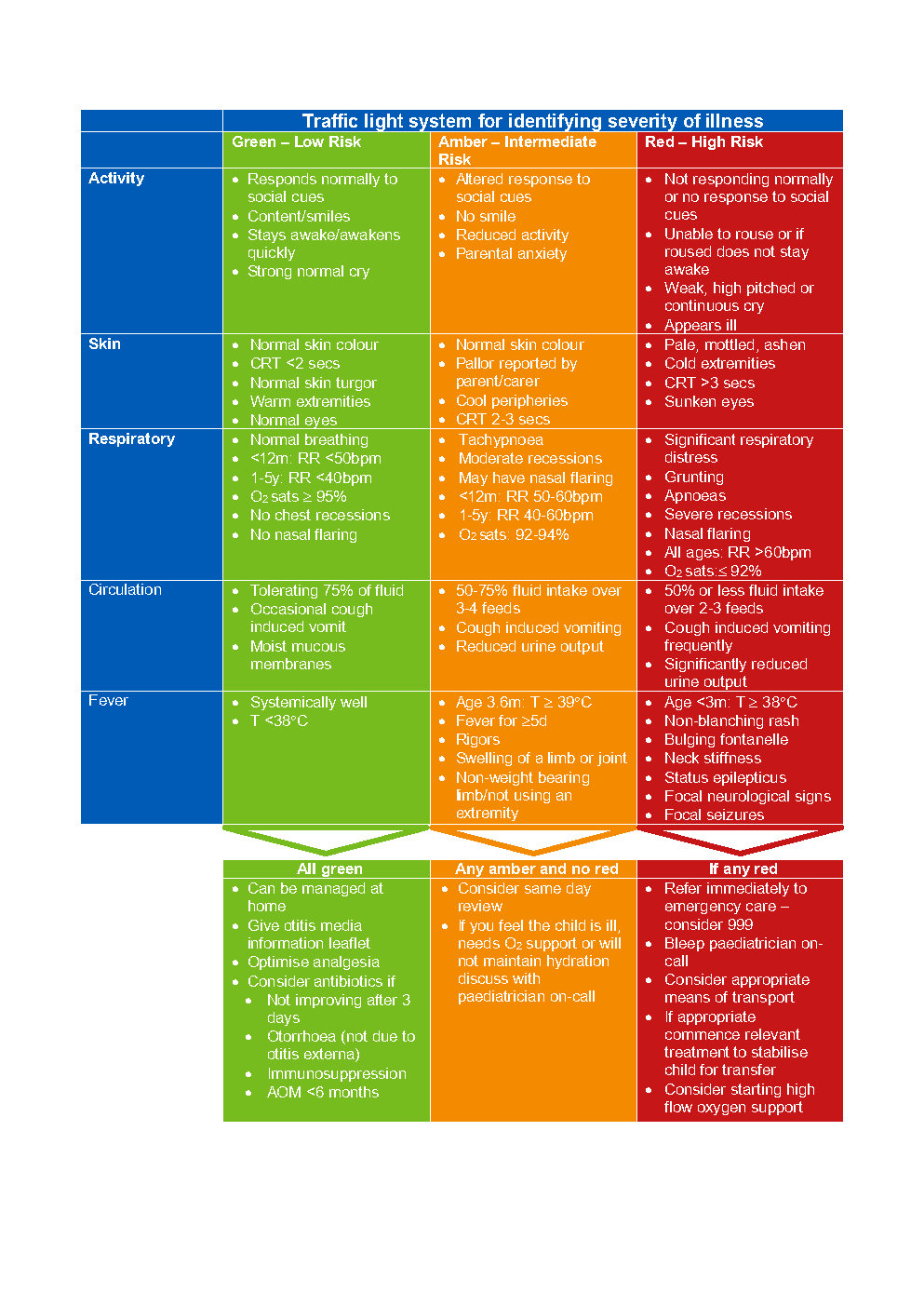
Paediatric Normal Values (adapted from APLS) |
|||
Age |
Resp Rate |
Heart Rate |
Systolic BP |
Neonate <4w |
40-6 |
120-160 |
>60 |
Infant <1 y |
30-40 |
110-160 |
70-90 |
Toddler 1-2 yrs |
25-35 |
100-150 |
75-95 |
2-5 yrs |
25-30 |
95-140 |
85-100 |
Red Flag Symptoms
Exclude Red Flag Symptoms
- Features of mastoiditis
- Intracranial infection can occur in absence of mastoiditis, signs include
- Increasing drowsiness
- Meningism/irritability
- Severe headache persisting despite regular analgesia or worse on lying down/in the morning
- Persistent vomiting
- Severe retroorbital pain
- New onset squint or diplopia – covering up one eye
- Deteriorating vision – complaining of blurred vision
- New limb weakness – may exhibit change of hand preference
- Unsteady gait or coordination issues
- Pain beyond ears, extensive headache or facial pain
- Haemodynamic instability/shock
Low Threshold for Admission
- Age <3 months
- Age 3-6 months with temperature ³ 39°C
- Craniofacial syndromes, e.g. Down’s syndrome, cleft palate
- Immunodeficiency
- Cochlear implant
Guidelines on Management
General Points
- One of the most common diseases in infants and children
- Peak incidence between 6 and 15 months; 75% occur in children under 10 years
- Usually a self-limiting infection and most will experience symptom resolution within 4-7 days with symptomatic treatment only
- Respiratory viral infections usually precede or coincide with AOM in children
- Complications are rare in otherwise health patients from developed countries
Differential Diagnoses
Clinical Feature |
Otitis Externa |
Otitis Media |
Ear pain |
Yes |
Yes, often improved when |
Discharge |
Scanty |
Mod/severe mucopurulent |
Hearing |
Later onset muffled |
Early onset |
Preceding URTI |
No |
Often |
Tender ear canal |
Yes, very |
No |
Periauricular swelling |
Yes in severe secondary to soft tissue cellulitis |
No unless mastoiditis |
Canal swelling |
Yes |
No |
Ear drum |
Can be difficult to visualise due to canal debris |
Red bulging, oedematous, |
Associated with intracranial complication |
No (unless immunocompromised) |
Yes |
Assessment
- New/rapid (days) onset earache and associated loss or reduction in hearing
- In younger children
- Pulling, tugging or rubbing of the ear
- Non-specific symptoms, e.g. fever, irritability, crying, poor feeding, restlessness at night, cough, rhinorrhoea
- Otoscopic appearance: bulging tympanic membrane with loss of landmarks, changes in membrane colour (red or yellow), perforation, discharge of pus
- Examine mastoid for tenderness, erythema and swelling
- Note any cervical lymph node enlargement
Referral Criteria/Information
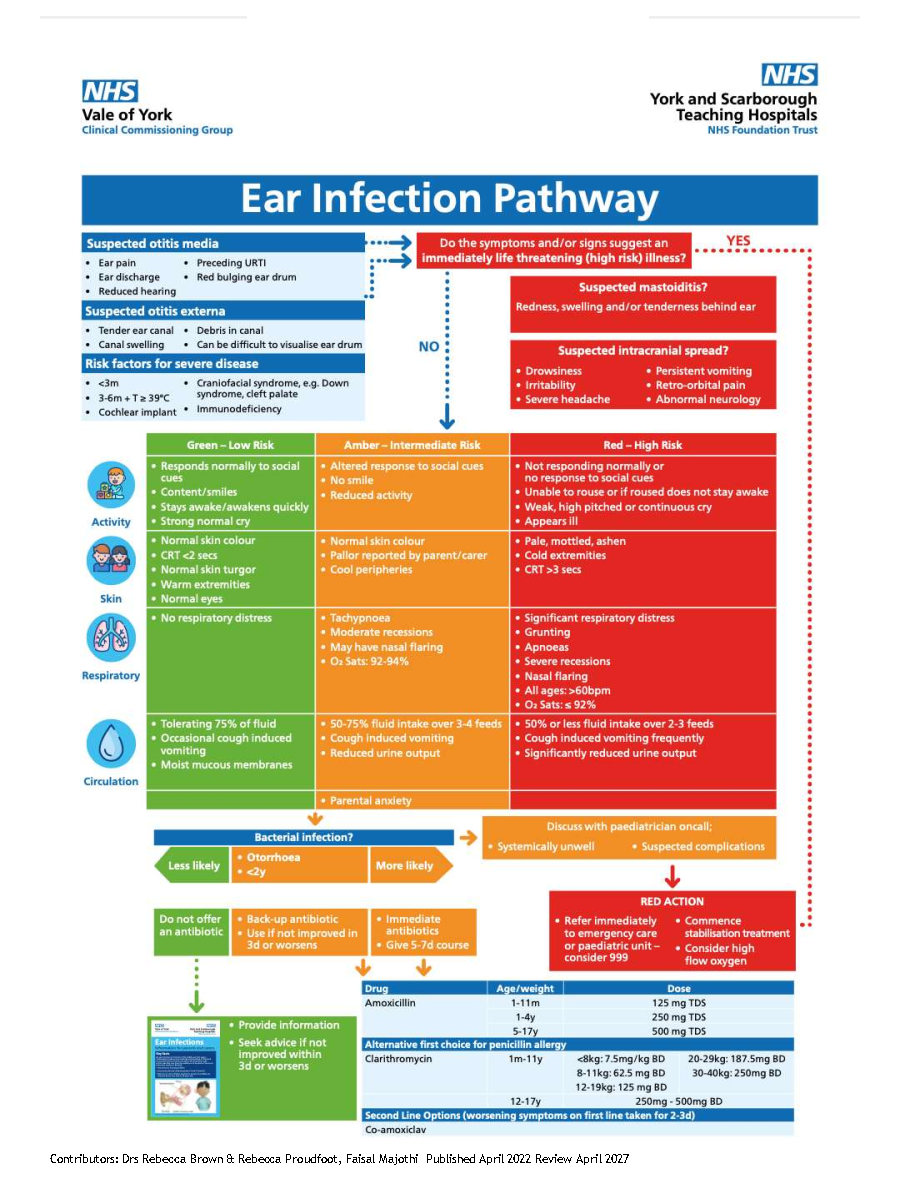
When to Arrange Emergency Hospital Admission
- Severe systemic infection
- Suspected complications of AOM such as meningitis, mastoiditis, intracranial abscess, sinus thrombosis or facial nerve paralysis
Low Risk for Community Management
- No antibiotics: seek advice if symptoms worsen rapidly or significantly, do not improve after 3 days or becomes systemically unwell.
- Delayed antibiotics: start if symptoms do not start to improve within 3 days. Seek medical advice if symptoms worsen rapidly or significantly
- Immediate antibiotics: Give a 5-7 day course.
Community Antibiotic Treatment
Antimicrobial therapy should considered in the following groups
- Otorrhoea
- Age <2y with bacterial infection
Drug |
Age |
Weight |
Dose |
First Line Options |
|||
Amoxicillin |
1-11m |
125 mg TDS |
|
1-4y |
250 mg TDS |
||
5-17y |
500 mg TDS |
||
Can be added if there is no response to Amoxicillin. Use first line if penicillin allergic |
|||
Clarithromycin |
1m-11y |
<8kg |
7.5mg/kg BD |
8-11kg |
62.5 mg BD |
||
12-19kg |
125 mg BD |
||
20-29kg |
187.5mg BD |
||
30-40kg |
250mg BD |
||
12-18y |
250mg BD |
||
Second Line Options (should be used in pneumonia associated with influenza) |
|||
Co-amoxiclav |
1-11m |
0.25ml/kg of 125/31 suspension TDS |
|
1-5y |
5ml of 125/31 suspension TDS |
||
6-11y |
5ml of 250/62 suspension TDS |
||
12-17y |
250/125mg or 500/125mg tablets TDS |
||
Seek microbiologist advice in penicillin allergy |
|||
Referral Information
Indications for referral to ENT
- If ear discharge (otorrhoea) persists for 2 weeks
- If perforation of the tympanic membrane has occurred
- If hearing loss persists in the absence of pain or fever
- Recurrent acute otitis media (³3 episodes in 6m or ³4 episodes in 12m)
Additional Resources & Reference
Patient information leaflets/ PDAs
References
- National Institute for Clinical Excellent [NICE] (2018) Otitis media (acute): anrtimicrobial prescribing NG91[Viewed 12 Nov 2021] https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng91
- Venekamp RP, Sanders SL, Glasziou PP et al. Antibiotics for acute otitis media in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2015; https://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD000219.pub4: CD000219.
- Venekamp RP, Damoiseaux RA, Schilder AG. Acute otitis media in children. BMJ Clin Evid 2014; 2014.
- Lording A, Patel S, Whitney A. Intracranial complication of ear, nose and throat infections in childhood. Journal of ENT Masterclass 2017; 10: 64-70.
- Patel S, et al. Paediatric Pathways: Acute Otitis Media (AOM) and Mastoiditis Pathway for Children Presenting to Hospital. British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy https://bsac.org.uk/paediatricpathways/otitis-media-mastoiditis.php [Viewed 12 Nov 2021]
Associated Policies
Specialties
Places covered by
- Vale of York
Hospital Trusts
- York and Scarborough Teaching Hospitals