Bronchiolitis
Definition/Description
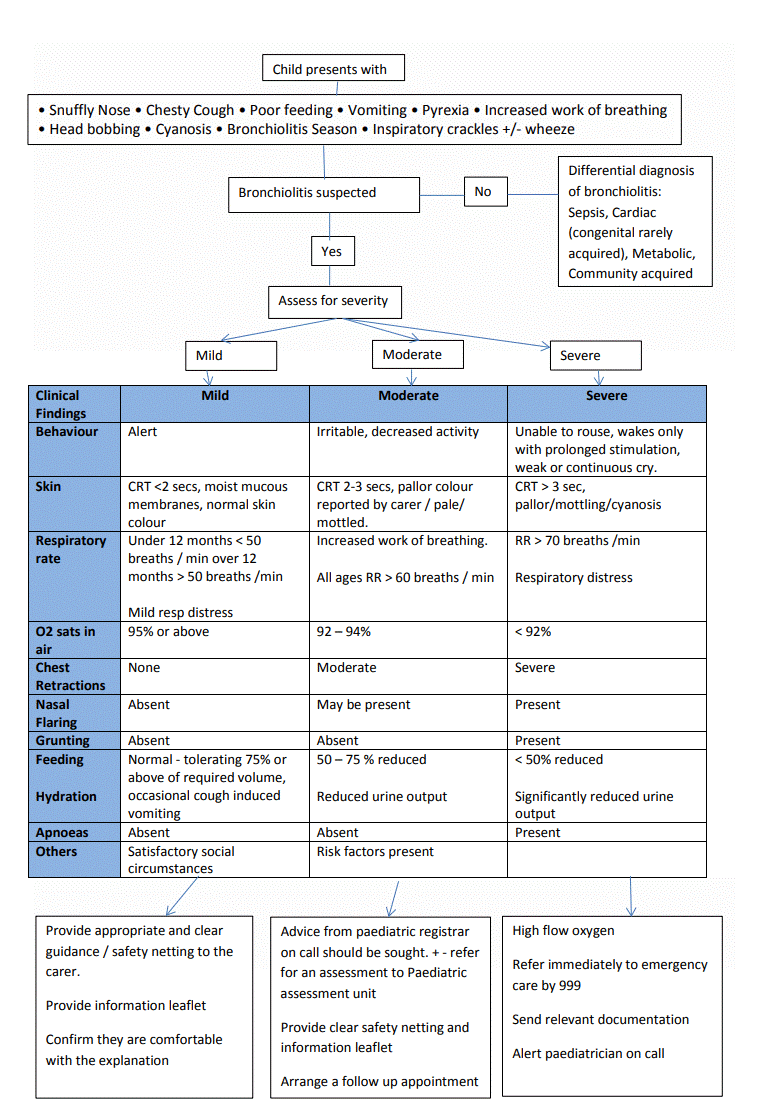
An acute viral infection causing coryza, cough and wheeze. The average age of a child with bronchiolitis is 3-6 months, but it can occur in a child from the first week of life up to 2 years of age.
Red Flag Symptoms
Risk factors for severe bronchiolitis include:
- Chronic lung disease
- Congenital heart disease
- Age under 3 months
- Premature birth (especially under 32 weeks)
- Neuromuscular disorders
- Immunodeficiency syndromes
- Smoking increases severity of the illness
Management of bronchiolitis is purely symptomatic i.e. feeding support, suction as required, oxygen and close monitoring if associated co-morbidities.
There is NO evidence for any of the following treatments:
- Chest physiotherapy on children who do not have an underlying chest problem
- Antibiotics
- Hypertonic saline
- Nebulised adrenaline
- Salbutamol
- Montelukast
- Ipratropium
- Systemic or inhaled corticosteroids
Guidelines on Management
Referral Criteria/Information
No Referral/Information Listed
Additional Resources & Reference
Associated Policies
There are no associated policies.
Specialties
There are no associated specialties.
Places covered by
- East Riding
- Hull
Hospital Trusts
- Hull University Teaching Hospitals
Date created:
31/07/2025, 14:41
Last modified:
31/07/2025, 14:41
Date of review:
29/07/2025