CDC Atrial Fibrillation (NL & NEL)
Definition/Description
No Definition/Desription Listed
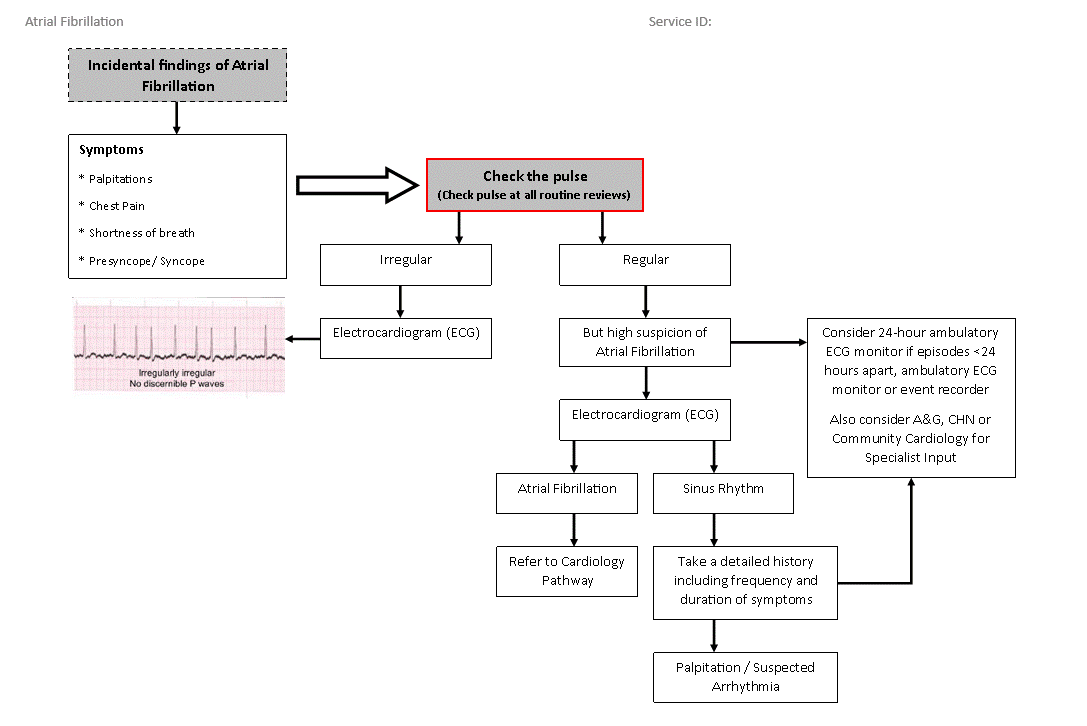
Red Flag Symptoms
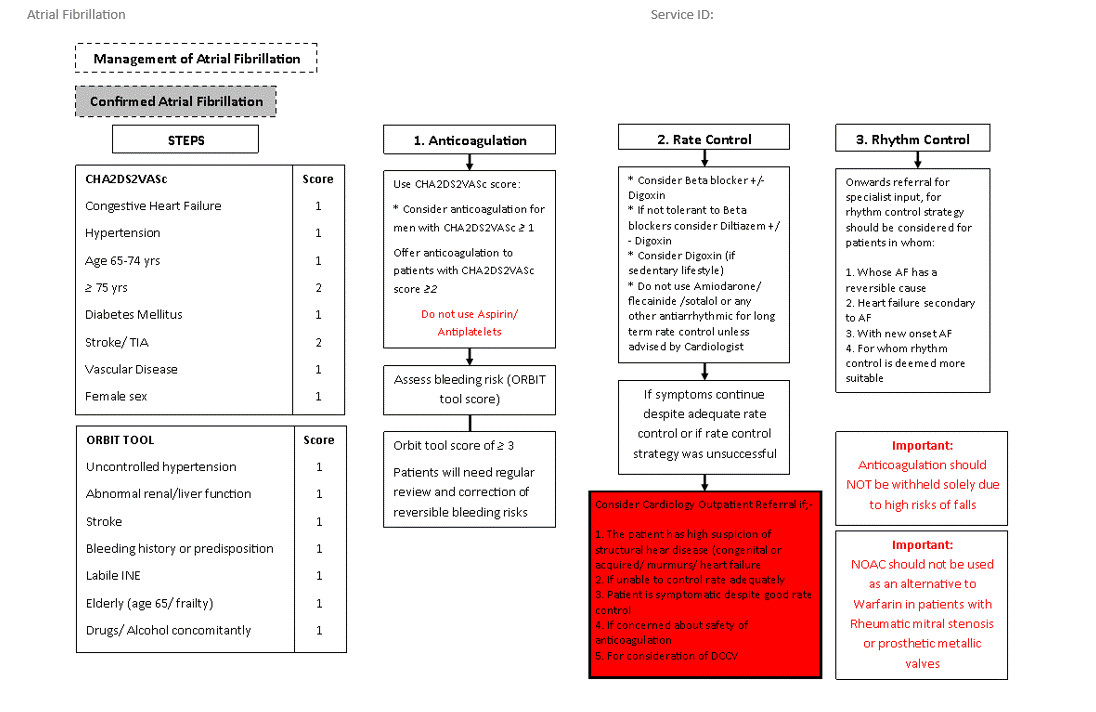
Atrial Fibrillation Stroke Risk Factors:
Use the CHA2DS2VASc stroke risk score to assess stroke risk in people with any of the following:
- Symptomatic or asymptomatic paroxysmal, persistent, or permanent atrial fibrillation
- Atrial flutter
- A continuing risk of arrhythmia recurrence after cardioversion back to sinus rhythm or catheter ablation
Atrial Fibrillation Bleeding Risk Factors:
Assess the risk of bleeding when:
- Considering starting anticoagulation in people with atrial fibrillation and
- Reviewing people already taking anticoagulation
- Use the ORBIT bleeding risk score because evidence shows that it has a higher accuracy in predicting absolute bleeding risk than other bleeding risk tools. Accurate knowledge of bleeding risk supports shared decision making and has practical benefits, for example, increasing patient confidence and willingness to accept treatment when risk is low and prompting discussion of risk reduction when risk is high. Although ORBIT is the best tool for this purpose, other bleeding risk tools may need to be used until it is embedded in clinical pathways and electronic systems. [2021]
Offer monitoring and support to modify risk factors for bleeding, including:
- Uncontrolled hypertension
- Poor control of international normalised ratio (INR) in patients on vitamin K antagonists
- Concurrent medication, including antiplatelets, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Harmful alcohol consumption
Reversible causes of anaemia
Guidelines on Management
|
||||
| Responsibilities | CDC Basket Name | To include |
|
|
|
Primary care initial investigations for AF | ECG | ||
| Specialist care | CDC investigations for AF | ECG | ||
Please note:
- There are 3 specialist routes into this pathway which are CHN, Specialist care and Secondary care
- If bloods have been taken within the last 3 months, they do not need to be repeated
- ECG cab be undertaken in the GP practice or within the CDC, whichever is the most suitable for the patient
Referral Criteria/Information
No Referral Criteria/Information Listed
Any Other Information
Request Transthoracic Echocardiogram
- In patients with high risk or suspicion of underlying structural or functional heart disease (e.g. murmurs, congenital heart disease and previous myocardial infaction / cardiomyopathy)
- In patients whom refinement of clinical risk stratification for anticoagulation therapy is needed
- For whom a rhythm control strategy is considered including DC cardioversion / ablation / initiation of antiarrhythmics such as flecainide
DVLA and Atrial Fibrillation (cars and motorcycles)
- Driving must cease if arrhthmia has caused or likely to cause incapacity
- Driving may be permitted when underlying cause has been identified and controlled for at least 4 weeks
- DVLA not to be notified unless there are disabling and distracting symptoms
- For further information please refer to the DVLA guidelines
Associated Policies
There are no associated policies.
Specialties
Places covered by
- north-east-lincolnshire
- north-lincolnshire
Hospital Trusts
Date created:
11/07/2025, 06:51
Last modified:
15/07/2025, 10:02
Date of review: